PS2 Homebrew Pt. 1
Welcome!
In this series of tutorials, we will be going over how to create homebrew apps for the PS2!
This first tutorial will go over setting up a PS2 development toolchain to aid us in developing executables for the PS2.
There are two methods of installing the open source PS2 SDK and the choice is yours.
The Docker installation allows a developer to setup an environment separate from the host OS in which components are installed, allowing any host OS to compile and run homebrew toolchains with trivial dependency management.
Docker install
On Windows, download Docker Desktop which will provide you with the Docker GUI and Docker CLI which is powered by the Docker Engine.
On Linux-like systems, Docker is usually installable through the docker-cli package.
In a terminal or command prompt, type the following command to download the PS2DEV image:
docker pull ps2dev/ps2dev
Note: This may require sudo/administrator privileges. Docker can be installed in a rootless manner.
Local install
A local install of the PS2DEV toolchain is a lot more involved compared to the Docker installation method.
Install prerequisites
The installation of a PS2DEV toolchain requires the following dependencies:
gcc, make, cmake, patch, git, texinfo, flex, bison, gettext, wget, gsl, gmp, zlib, mpfr and mpc.
A detailed list of installation instructions for each OS is available in the README.MD file of the PS2DEV repo available here.
Setup environment variables
Copy the following code into ~/.bashrc:
export PS2DEV=/usr/local/ps2dev
export PS2SDK=$PS2DEV/ps2sdk
export GSKIT=$PS2DEV/gsKit
export PATH=$PATH:$PS2DEV/bin:$PS2DEV/ee/bin:$PS2DEV/iop/bin:$PS2DEV/dvp/bin:$PS2SDK/bin
After modifying your login script, make sure to source the login script to ensure these
environment variables are set. Alternatively, log out and log back in.
source ~/.bashrc
Now create the standard toolchain directories:
sudo mkdir -p $PS2DEV
sudo chown -R $USER: $PS2DEV
Note: The space here is intentional and is necessary.
Clone the toolchain
The toolchain repo can be cloned with the following Git command:
git clone https://github.com/ps2dev/ps2dev.git
This command will clone the contents of the PS2DEV repo into the ps2dev folder.
Afterwards, you can change directory to the ps2dev repo and execute the following commands to build the toolchain from start to finish.
./build-all.sh
Compiling a test program
On the host OS, create a folder named test in a folder (e.g. the Desktop), this is where all the code for the program will go.
Inside the folder, create a file named Makefile and a main.c source file which will hold the source code
for our program.
Copy the following code to the Makefile with a text editor:
TOOLCHAIN = mips64r5900el-ps2-elf
CC = $(TOOLCHAIN)-gcc
all: main.elf
main.elf: main.c
$(CC) main.c -T$(PS2SDK)/ee/startup/linkfile -o main.elf
clean: main.elf
rm main.elf
In the main.c file, add the following code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
puts("Hello, World!");
// Infinite loop
// This is to allow the user to monitor the output
// in the serial console of an emulator.
for (;;) {
}
}
If you used the Docker installation, you can mount this folder at /test with a PS2DEV toolchain with the following command:
sudo docker run -it -w /test -v $(pwd):/test ps2dev/ps2dev sh
Otherwise, you can simply run make all to compile and test your program.
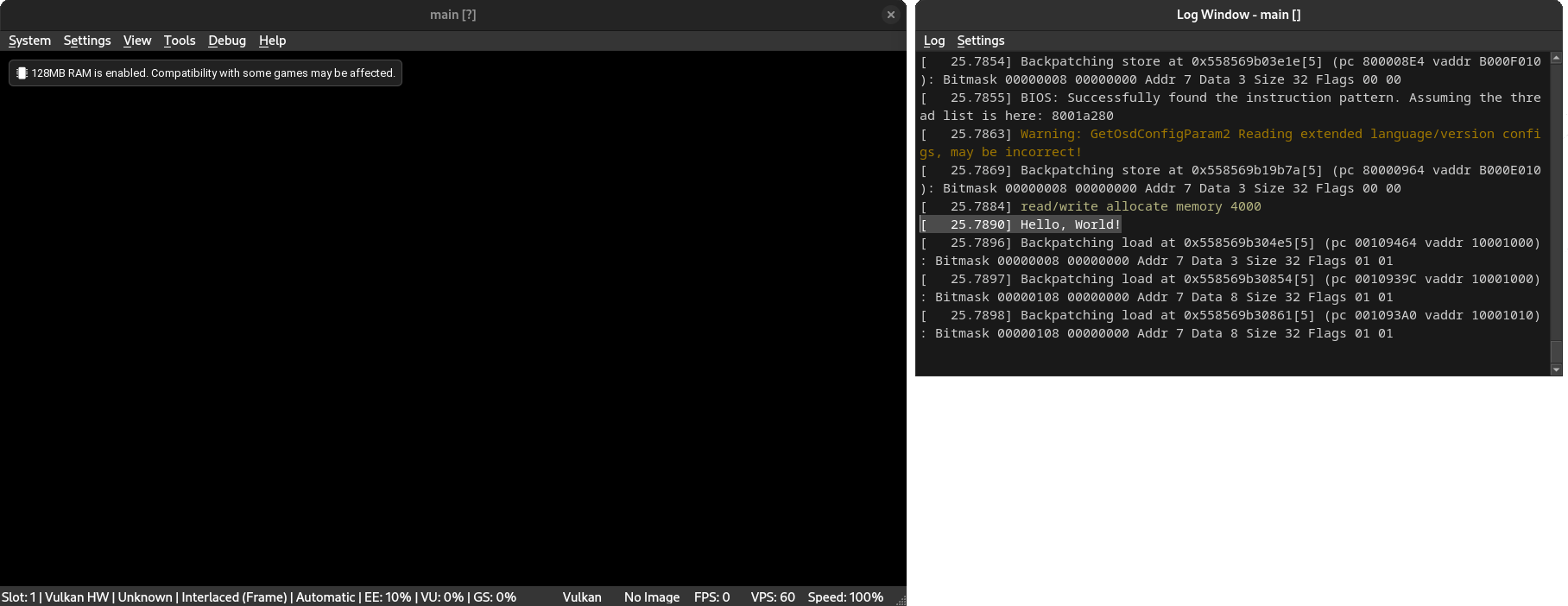
The main.elf executable file can be loaded into an emulator such as PCSX2.
If all went well, the following information should be printed to the IOP console. Prints via the EE are redirected to the IOP: